*This is a Washington State average for this occupation. Wage rates vary by employer, industry, experience and location. Source: Washington State Employment Security Department 2021 Occupational Employment and Wage Estimates.

What is a Machinist?
Almost every object you see in the world contains parts that are created by a machinist – from a desk to a car engine to the wings of an airplane. Like a sculptor, a machinist uses high-tech cutting machines to shape metal, plastics, ceramics, composites and even wood into something new.
A machinist operates manually controlled and computer numerically controlled (CNC) machine tools such as lathes and milling machines, to cut and produce precision parts for machines, instruments, and tools.
Machinists repair or produce parts using both manual and automated equipment with precise measurements. Essentially, a machinists’ goal is to ensure effective production operations and optimize procedures.

What are the Benefits of Becoming a Machinist
Machinist is an advanced apprenticeship occupation that reinforces manual and CNC machining skills along with computer aided design and precision measuring.
Upon completion of a Machinist apprenticeship, you will receive a nationally-recognized journey-level credential and can move onto more advanced occupations such as CNC Programmer, Tool & Die Maker, and Maintenance Technician.
As a Machinist, you will enjoy a long-term career with a good salary, job advancement opportunities, and the chance to work with your hands and cutting-edge technology.
Step to Becoming an Apprentice
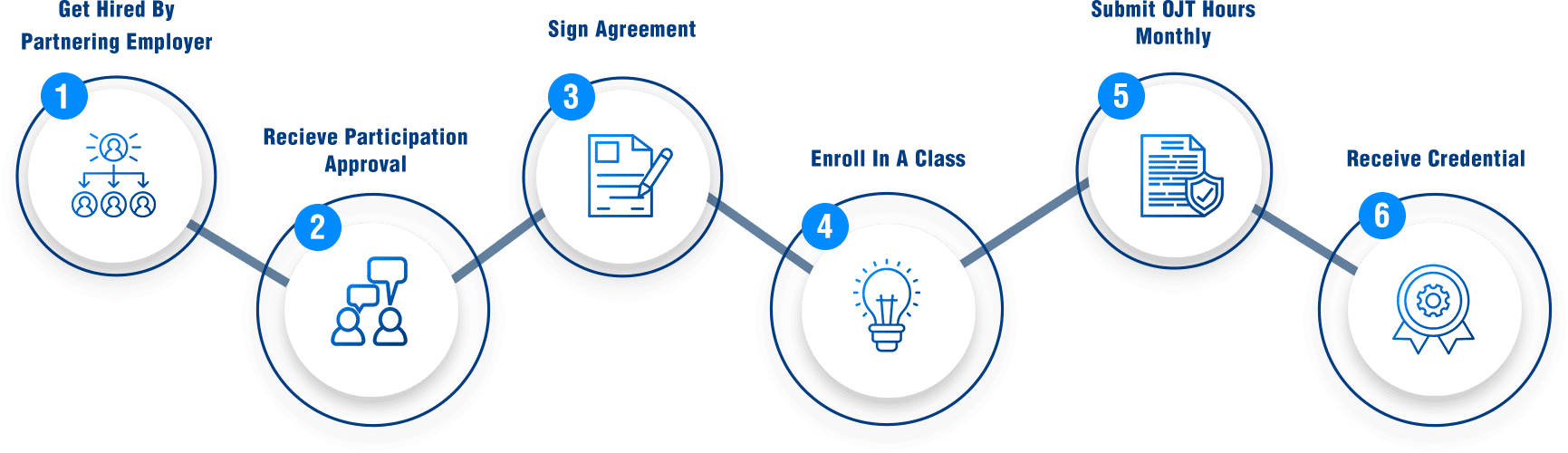

6 Steps to Becoming an Apprentice
Get Hired by a Participating Employer AJAC Partners With
Receive Participation Approval from Your Employer
Sign an Apprenticeship Agreement with AJAC
Enroll in AJAC’s Apprenticeship Classes Each Quarter
Log and Submit Your OJT Hours Monthly
Receive a Nationally-Recognized Journey-Level Certification from L&I
How Much Can I Earn?
Where Will I Work?
AJAC has partnered with 300+ advanced manufacturers to provide supervised, structured, paid on-the-job training.
AJAC apprentices can only work for companies that agree to hire them and place them into the program.
Each company has their own methodology for who they select as an apprentice.

Where Are Classes Held?
Classes are held one night a week, typically on a Tuesday, Wednesday, or Thursday from 5:00 pm to 9:00 pm.
AJAC’s apprenticeships classes are structured for both online learning or in-person learning. Depending on the specific class you are taking, you may be required to complete it online or in-person.
In-person classes are held either a local community/technical college, high school, or skills center.
Apprenticeship Classes
Machinists apprentices take 12 college-level classes. Each class consists of 50 hours of lecture and/or practical application. Upon completion of each class, apprentices will receive 5 college credits.
As a registered apprentice, you automatically receive 50% reduced tuition. Over half of AJAC’s partnering employers elect to pay for their apprentice’s tuition, making the entire apprenticeship free-of-cost.
Currently, each class costs $300 out-of-pocket.
Fundamental manual machining skills and knowledge to include topics such as job plans, drawings, tolerances, engineering specifications and use of manual tools.
Intro to precision machining with a focus on basic, manual machining techniques including speeds and feeds, milling machine/drill press and lathes.
Learn to read and interpret engineering drawings and schematics, as well as practice basic drafting. Drawings studied in this class will come both from the text and from industry, and will include machining, fabrication, assemblies, and fluid power systems (only for Automation/Maintenance program).
Apprentices will develop a working knowledge and practical application of algebraic processes as they relate to manufacturing. They will identify and understand the applications of formulas to shop problems, learn to manipulate formulas, simplify expressions and solve linear equations. Discussions will include adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing fractions, ratio, proportion and percentages. Number lines and Cartesian coordinates will also be covered.
This course focuses on the fundamentals and applications of geometry and trigonometry. Topics include perimeters, areas, volume, trigonometric ratios and function, right angles and non-right angles. Apprentices will discuss relationships of lines, planes, angles, congruent and similar triangles, polygons and circles while performing geometric and trigonometric functions as they relate to manufacturing and aerospace. Other topics include special triangles and the Pythagorean Theorem.
G&M programing, reading G&M code, XYZ coordinates, establishing tool length offsets (TLO), calculating changed data capture (CDC) and cutter radius compensation (CRC).
Apprentices will study the theory and application of the use of standard tolerances and GD&T concentrating on geometric dimensioning and its relation to engineering drawings.
Apprentices will hand write simple commands and basic programs for mills using G & M codes. They will learn basic Mastercam and use of verification software.
Apprentices will hand write simple commands and basic programs for lathes using G & M codes. They will learn basic Mastercam and use of verification software.
Comprehensive understanding of outside processes and the properties of materials that are governed by industry standards.
Measuring and inspection of size, position, form, surface finish and orientation.
Exploration of new, emerging and advancing technologies, including properties and machining of composites. Apprentices will learn more in depth about Lean manufacturing, machine preparation, advanced machining technologies such as EDM, Water Jet and Laser Stereolithography.
On-the-Job Training Competencies
The table below is a schedule of tasks and hours designed as a guide. The 8,000 hours will be completed over the course of the apprenticeship. The apprentice shall be instructed and trained in all operations and methods customarily used on the various machines. Each company will adhere to the schedule as closely as facilities will permit in order to provide the apprentice with well-rounded experience and practice on all relevant equipment and processes in the shop.
| OJT Competency | Approx. OJT Hours |
|---|---|
| Conventional & CNC Machining Basics | 2,600 |
| Conventional & CNC Machining Operations | 2,100 |
| CNC Setup and Advanced Operation Procedures | 800 |
| Material Process, Quality Assurance & Cutting Technology | 500 |
| Advanced Machining Techniques & NC Basic Programming | 500 |
| Inspection, Parts Finishing, Deburr, Assembly, Bench Work | 1,500 |
| TOTAL HOURS | 8,000 |

Launch Your Career Today!
Submit your information using the link below. After we receive your information, an AJAC representative will contact you for next steps. Please note, this is not an official application to become an apprentice. After a partnering employers agrees to enroll you in the program, you will officially apply and enroll at that time.
