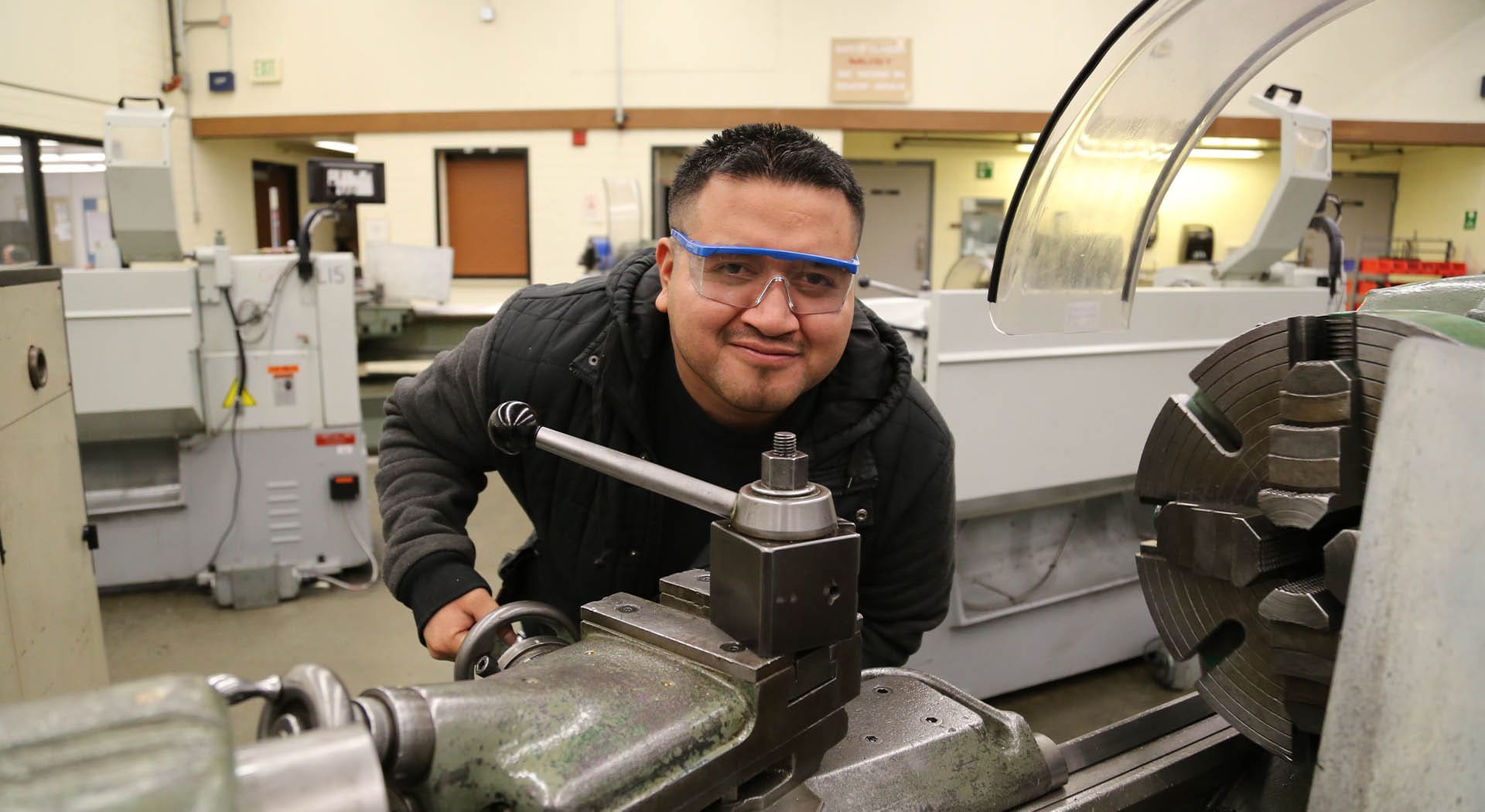
A Tool & Die Maker is a highly skilled craftsperson who designs, fabricates, and maintains the specialized tools, dies, and molds used in manufacturing. They turn blueprints and CAD designs into precision equipment that shapes, cuts, and forms parts for industries ranging from aerospace to space exploration.
What Does a Tool and Die Maker Do?
Program Overview
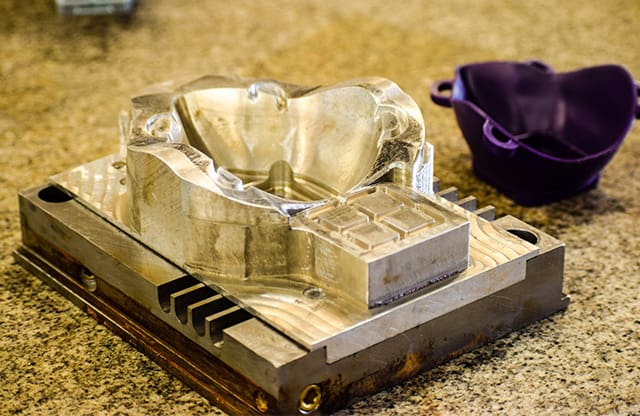

Train for a Career as a Tool and Die Maker
As a Tool & Die Maker apprentice, you’ll work with advanced machinery and fabrication tools to create the essential tooling, dies, and molds behind modern manufacturing.
From aerospace components to high‑precision industrial parts, your hands‑on skills will drive innovation and quality.
| Program Length | 5-Years |
| On-the-Job Hours | 10,000 |
| College Classes | 15 |
| College Credits | 75 |
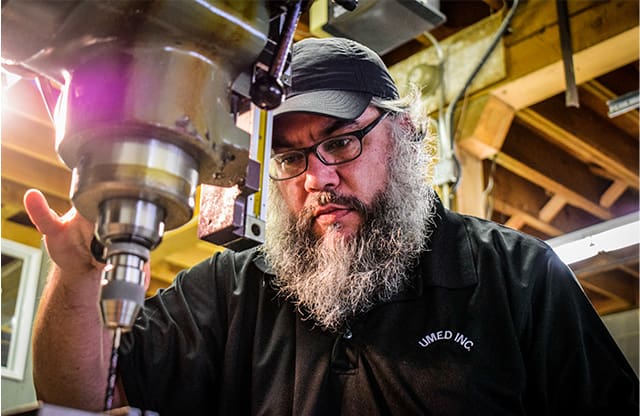

Hands-On Training That Builds Real Skills
Tool & Die Makers are at the heart of precision manufacturing.
You’ll learn to:
- Read blueprints, sketches, specifications or CAD/CAM files for creating tooling and dies.
- Set up, operate and disassemble conventional, manual, and CNC machine tools including mills, lathes, grinders.
- File, grind and adjust parts so they fit together properly and meet tight tolerances.
- Test completed tools and dies to ensure they meet specifications and perform under production conditions.
Every precision‑manufacturing operation depends on accurate tooling — you’ll build those tools.
Why Apprenticeship Makes Sense
Hands-On Training with Real Employers
AJAC has partnered with 300+ advanced manufacturers to provide supervised, structured, paid on-the-job training.
AJAC apprentices can only work for companies that agree to hire them and place them into the program.
Each company has their own methodology for who they select as an apprentice.
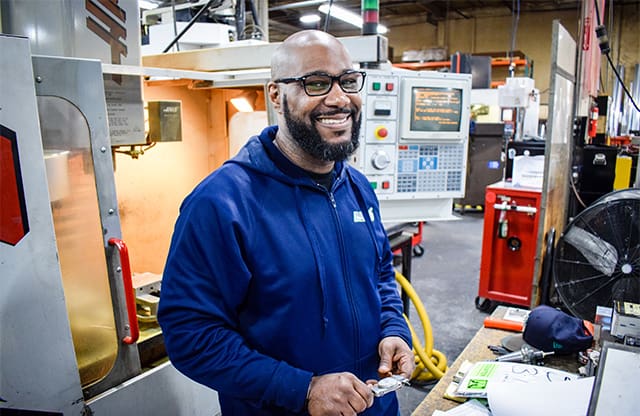

Earn a Paycheck While You Learn
This advanced apprenticeship gives you deep machining, design, and fabrication skills — opening the door to high‑paying, in‑demand careers.
Program Highlights:
- Earn while you learn – full‑time work with on‑the‑job training
- 50% reduced tuition — many employer partners cover full cost
- Earn college credits in each class while you train
- Receive a nationally‑recognized journey‑level credential upon completion
- Career paths into Operations Manager, Maintenance Manager, CNC Programmer, or Tool & Die Lead roles
*This is a Washington State average for this occupation. Wage rates vary by employer, industry, experience and location.
Apprenticeship Classes
Classes are held one evening per week (Tuesday–Thursday, 5–9 PM) and are available online or in person at local colleges, high schools, or skill centers. Tuition: $400 per class (50% reduced rate). Many employers pay the full cost. This schedule allows you to work full‑time and complete your classroom training without disrupting your job.
Fundamental manual machining skills and knowledge to include topics such as job plans, drawings, tolerances, engineering specifications and use of manual tools.
Intro to precision machining with a focus on basic, manual machining techniques including speeds and feeds, milling machine/drill press and lathes.
Learn to read and interpret engineering drawings and schematics, as well as practice basic drafting. Drawings studied in this class will come both from the text and from industry, and will include machining, fabrication, assemblies, and fluid power systems (only for Automation/Maintenance program).
Apprentices will develop a working knowledge and practical application of algebraic processes as they relate to manufacturing. They will identify and understand the applications of formulas to shop problems, learn to manipulate formulas, simplify expressions and solve linear equations. Discussions will include adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing fractions, ratio, proportion and percentages. Number lines and Cartesian coordinates will also be covered.
This course focuses on the fundamentals and applications of geometry and trigonometry. Topics include perimeters, areas, volume, trigonometric ratios and function, right angles and non-right angles. Apprentices will discuss relationships of lines, planes, angles, congruent and similar triangles, polygons and circles while performing geometric and trigonometric functions as they relate to manufacturing and aerospace. Other topics include special triangles and the Pythagorean Theorem.
G&M programing, reading G&M code, XYZ coordinates, establishing tool length offsets (TLO), calculating changed data capture (CDC) and cutter radius compensation (CRC).
Apprentices will study the theory and application of the use of standard tolerances and GD&T concentrating on geometric dimensioning and its relation to engineering drawings.
Apprentices will hand write simple commands and basic programs for mills using G & M codes. They will learn basic Mastercam and use of verification software.
Apprentices will hand write simple commands and basic programs for lathes using G & M codes. They will learn basic Mastercam and use of verification software.
Comprehensive understanding of outside processes and the properties of materials that are governed by industry standards.
Measuring and inspection of size, position, form, surface finish and orientation.
Exploration of new, emerging and advancing technologies, including properties and machining of composites. Apprentices will learn more in depth about Lean manufacturing, machine preparation, advanced machining technologies such as EDM, Water Jet and Laser Stereolithography.
Design jigs, fixtures, and gauges for a variety of manufacturing applications.
Apprentices will learn to design dies for power presses that pierce, blank, punch, and form materials. They will learn about important design considerations for die components, which include die blocks, gauges, punches, punch plates, strippers, stops, fasteners, and die sets. Apprentices will gain practical, hands-on design experience by completing a design project.
Exploration of the materials, processes, and mold design principles for injection molding, compression molding, transfer molding, and die casting.
10,000 Hours of Hands-On Experience
Apprentices gain hands-on experience with structured tasks to ensure well-rounded expertise:
| OJT Competency | Approx. OJT Hours |
|---|---|
| Bench Work | 1,400 |
| Milling Machine | 1,600 |
| Engine Lathe | 1,000 |
| Grinder (Surface Tool) | 1,000 |
| Heat Treating | 400 |
| Electric Discharge Mach. OPR. (EDM) | 800 |
| Tool Layout and Design | 1,000 |
| CNC Programming & Operations | 1,200 |
| Jig Bore and Grinding | 200 |
| Drilling Machines | 400 |
| Shop Maintenance and Review | 800 |
| Tool Steel Welding | 200 |
| TOTAL HOURS | 10,000 |
Step to Becoming an Apprentice
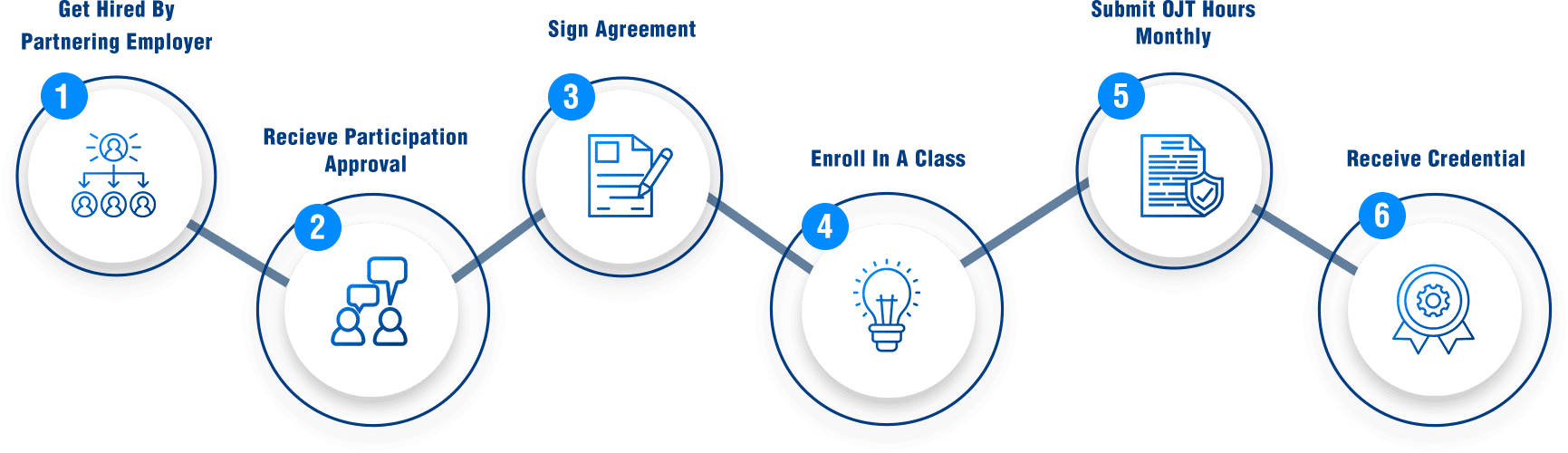

6 Steps to Becoming an Apprentice
Find an Employer Partner: Apply to a company already partnered with AJAC — or, if your employer isn’t yet a partner, they can easily join the program. The process is simple and AJAC will guide them through every step.
Get Company Approval: Your supervisor signs off on apprenticeship participation.
Sign the Apprenticeship Agreement: AJAC visits your employer to finalize.
Start Classes: Enroll in your first college-level course.
Track Hours: Log on-the-job training through AJAC’s Apprentice Tracking System.
Graduate: Earn your Journey-Level Certificate and AJAC Certificate of Completion.

Your Career Starts Here
Ready to build precision tooling and molds, operate advanced CNC and machine tools, and become a master in manufacturing? Join AJAC’s Tool & Die Maker apprenticeship — earn while you learn, build skills, earn college credits, and walk away with a nationally‑recognized credential.
